Working Principle of Sealing Elements
- Home
- Pneumatic Sealing Elements
- Working Principle of Sealing Elements
Sealing elements are designed for the pressurized gas not to pass to the un-pressurized side in pneumatic systems. Pneumatic cylinders are widely used in mechanical applications that require low forces with high reciprocating sliding speeds. Sealing elements are one of the most important parts of these cylinders.
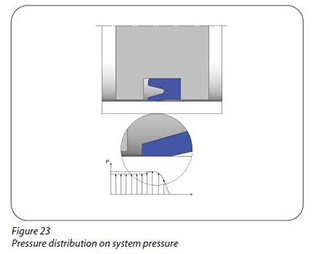
The sealing elements are being installed into the respective groove with a preload. Figure 22 shows the sealing element, preloaded after the assembly of the seal and the free space needed in the housing. The sealing element is able to work in low pressures due to this preload. Figure 23 shows the pressurized air filling into the groove and sealing element is expanded with this pressure.
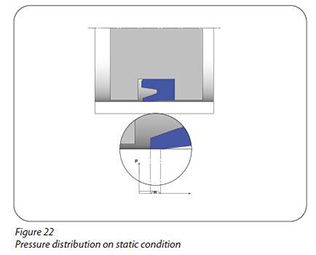
Sealing elements are produced from such materials that can change their form when force is applied (Figure 23) and can return to the original form when this force dissapears (Figure 22). In this respect sealing elements are produced from elastomers, thermoplastics or thermoplastic elastomers.
Sealing elements do have more than one duty in pneumatic cylinder due to the limited space and the cost. That’s why most of the rod seals work both as a wiper and a rod seal. In piston sealing elements, the designs are used to avoid the necessity of having a piston itself.